Two research programmes of the Federal Office of Energy have published new calls. One of the call topics is a collaboration between the two programmes. Weiterlesen
Schlagwortarchiv für: Climat
SuisseEnergie pour les communes – Soutien accordé à 557 communes
Pour la troisième fois déjà, l’OFEN apporte son soutien, par le biais du programme de soutien «SuisseEnergie pour les communes», aux villes, communes et régions qui veulent faire avancer activement leur politique climatique et énergétique. Les champs d’action des projets communaux et régionaux concerne les secteurs du bâtiment, des énergies renouvelables, de la mobilité ainsi que des services et processus industriels. L’appel à projets de 2025 se focalisait sur deux thèmes prioritaires: «zéro net / énergie hivernale» et «micromobilité». Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenGrande Dixence : 75 ans sous la surveillance attentive de la Confédération
En 1950, la société Grande Dixence SA voyait le jour à Sion, avec pour mission de construire et d’exploiter ce qui allait devenir le plus grand aménagement hydroélectrique de Suisse. Alors que l’entreprise célèbre son 75e anniversaire cette année, c’est aussi l’occasion de mettre en lumière le rôle de l’Office fédéral de l’énergie (OFEN), garant de la sécurité des grands barrages suisses depuis plusieurs décennies. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenAs EU climate policy tightens, its Green Deal increasingly shapes Swiss energy and emissions through shared infrastructure – long-standing hydropower integration, electricity lines and gas pipelines –, Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) linkage and EU-wide clean fuel and CO2 regulations. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenDas Schweizer Energiesystem für künftige Risiken wappnen
Wie stark Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft von der Energieversorgung abhängig sind, hat das Blackout Ende April auf der spanischen Halbinsel gezeigt. Eine Energieinfrastruktur, die auf künftige Gefahren vorbereitet ist und Menschen, die mit kritischen Situationen umgehen können, sind deshalb von grosser Bedeutung. Weiterlesen




 1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00
1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00If waste heat is continuously generated from an industrial process and steam is required at the same time to complete the process, the conditions are favorable for the use of a steam-generating heat pump. A team of researchers from the University of Applied Sciences of Eastern Switzerland has investigated the conditions for the success of this energy-efficient and climate-friendly form of heat supply. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenExamen approfondi de l’AIE: Zoom sur la politique énergétique de la Turquie
En avril 2025, l’Agence Internationale de l’Énergie (AIE) a conduit une nouvelle revue approfondie (In-Depth Review) de la politique énergétique de la Turquie, à laquelle Frédéric Maurer, spécialiste en efficacité énergétique à l’Office fédérale de l’énergie (OFEN) a pu participer. Ce processus, conduit en collaboration avec les autorités turques, offre un instantané stratégique de la trajectoire énergétique d’un pays ayant l’ambition de devenir un hub énergétique régional et situé à la croisée des chemins entre l’Europe, l’Asie et le Moyen-Orient. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenÉlectricité, pétrole, uranium: les importations énergétiques de la Suisse
La Suisse importe actuellement 70% de l’énergie qu’elle consomme. Bien que les importations d’énergie soient en baisse, la sécurité de l’approvisionnement énergétique repose toujours sur les marchés internationaux. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenWhat are the best policy measures to decarbonise Switzerland? A stand-alone carbon tax? A combination of taxes, subsidies, bans and standards? The DECARB project explores these questions and shows the advantages of combining measures to reach climate neutrality.
Academics typically recommend the introduction of a carbon tax to shift the economy away from fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. However, this policy proposal usually faces strong opposition from industry and the public, even if the revenues are fully redistributed.
In the DECARB project, a team of researchers investigated whether the use of other measures such as subsidies, standards or bans could facilitate the decarbonisation of Switzerland to an extent compatible with its goal of climate neutrality by 2050. In particular, it looked at how combining these measures into „instrument mixes“ might be superior to using just one of them, including the carbon tax. Overall, its findings suggest that mixes offer significant potential to advance climate policy.
DECARB is a research project sponsored by the EES programme and coordinated by the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
The project addresses the colossal challenge of decarbonising the Swiss energy system, including transport, residential buildings, and industry. Given that individual policy measures all have shortcomings, the project investigates how mixes of measures could enhance climate policy. Thanks to a pluri-disciplinary approach, DECARB identifies desirable mixes that would allow Switzerland to reach climate neutrality by 2050.
First, a review of the academic literature shows that there are several market failures, barriers to decarbonisation and policy constraints that justify the use of instrument mixes rather than a stand-alone carbon tax. While the desirable mixes differ across sectors, given the different target actors and technologies, some carbon tax is found to play a key role in all of them.
Second, using a mathematical model of the Swiss economy, the researchers show that the deep decarbonisation induced by the mixes has a negligible impact on gross domestic product (GDP), in the order of 1‰. When complementary instruments are included in the policy landscape, the carbon tax rate required to achieve an ambitious emissions target can be divided by about two. On the other hand, a stand-alone carbon tax allows for the highest rebate to households among the scenarios considered.
Third, using an online survey, the team provides evidence that Swiss citizens have a strong preference for instrument mixes rather than a stand-alone carbon tax. Language region, number and type of cars owned, and perceived threat of climate change are found to be important predictors of instrument preferences.
Full report: Cocker, F., Thalmann, P., Vielle, M., Vöhringer, F., Weber, S. (2024). DECARB – Mixes of policy instruments for full decarbonisation by 2050. Project funded by the Energy-Economy-Society (EES) research programme of the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE), Bern.
Authors: Fleance Cocker (EPFL), Philippe Thalmann (EPFL)
Shutterstock: ID: 2463945033; Doidam 10




 Noch keine Bewertungen
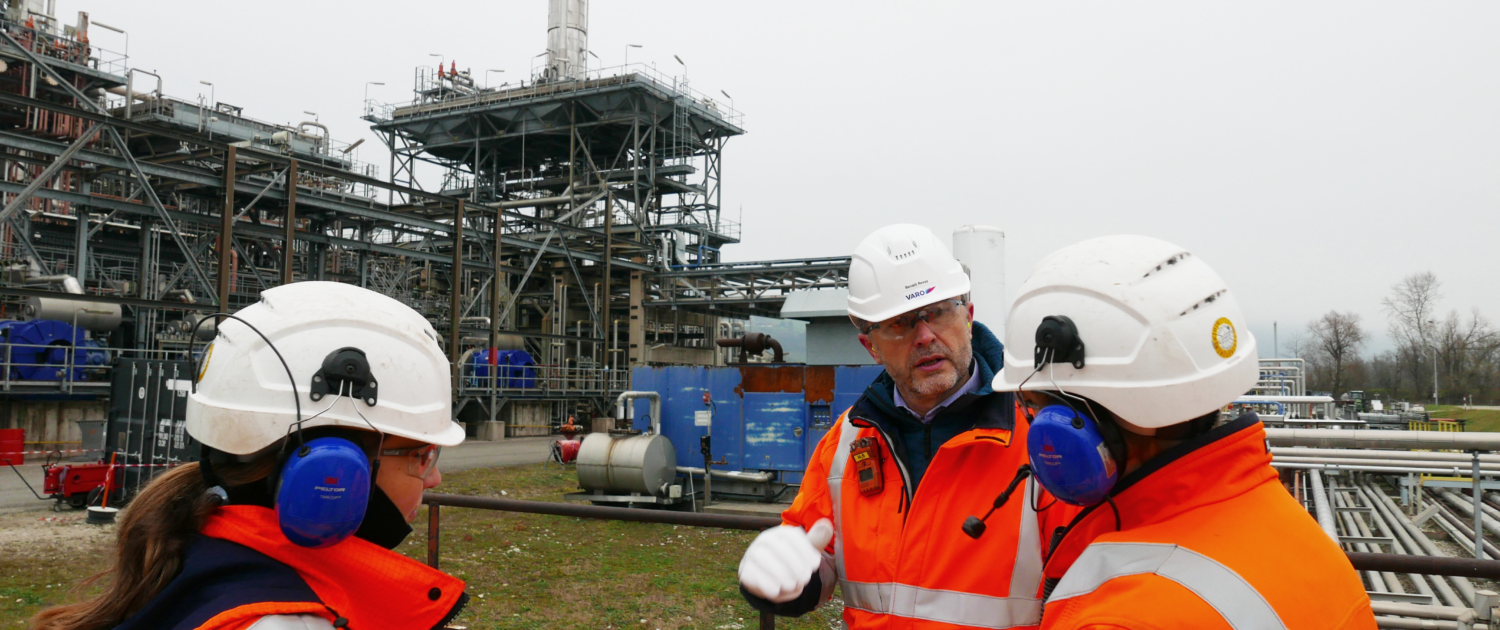
Noch keine BewertungenBenoît Revaz: immersion dans le monde des raffineurs de brut
Entre le Lac de Bienne et celui de Neuchâtel se trouve la dernière raffinerie de pétrole de Suisse. Depuis 2015, l’installation de l’entreprise VARO Energy est la seule installation de ce type dans notre pays après la fermeture des installations de Collombey en Valais. La raffinerie de Cressier (NE), mise en service en 1966, fournit environ 30% de la demande suisse en carburant et combustible fossile comme l’essence, le diesel, le mazout de chauffage ou encore du kérosène pour l’aviation. Elle compte 300 employés. Dans le cadre d’une de ses journées au cœur du travail des métiers de l’énergie, le directeur de l’Office fédéral de l’énergie s’est immergé dans le monde du raffinage. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenKontakt
Bundesamt für Energie
Pulverstrasse 13
3063 Ittigen
Postadresse:
Bundesamt für Energie
3003 Bern
Telefonnummern:
Hauszentrale +41 58 462 56 11
Pressestelle +41 58 460 81 52
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock Pixabay
Pixabay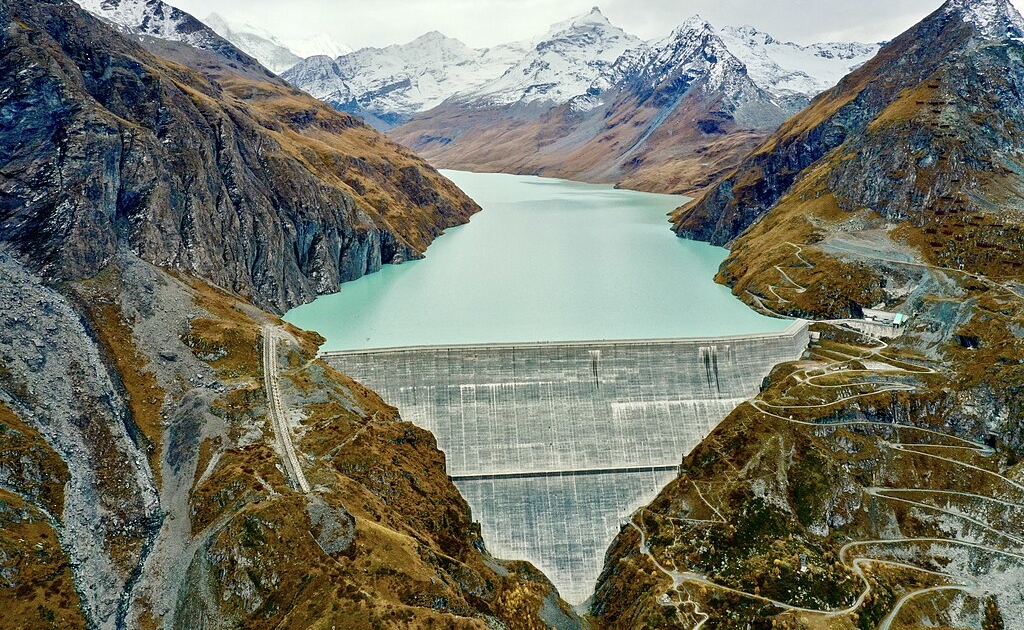 Jérémy Toma
Jérémy Toma Shutterstock
Shutterstock Shutterstock
Shutterstock Aneo Industry
Aneo Industry  Shutterstock
Shutterstock Shutterstock
Shutterstock shutterstock
shutterstock