As EU climate policy tightens, its Green Deal increasingly shapes Swiss energy and emissions through shared infrastructure – long-standing hydropower integration, electricity lines and gas pipelines –, Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) linkage and EU-wide clean fuel and CO2 regulations. Weiterlesen
Schlagwortarchiv für: policy
As the world shifts toward a more sustainable future, the role of finance in this transition has never been more critical. A project from ETH Zurich and the University of Zurich, supported by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy and published in February 2025, explored how Swiss private investors perceive and engage with sustainable finance. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenWhat are the best policy measures to decarbonise Switzerland? A stand-alone carbon tax? A combination of taxes, subsidies, bans and standards? The DECARB project explores these questions and shows the advantages of combining measures to reach climate neutrality.
Academics typically recommend the introduction of a carbon tax to shift the economy away from fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. However, this policy proposal usually faces strong opposition from industry and the public, even if the revenues are fully redistributed.
In the DECARB project, a team of researchers investigated whether the use of other measures such as subsidies, standards or bans could facilitate the decarbonisation of Switzerland to an extent compatible with its goal of climate neutrality by 2050. In particular, it looked at how combining these measures into „instrument mixes“ might be superior to using just one of them, including the carbon tax. Overall, its findings suggest that mixes offer significant potential to advance climate policy.
DECARB is a research project sponsored by the EES programme and coordinated by the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
The project addresses the colossal challenge of decarbonising the Swiss energy system, including transport, residential buildings, and industry. Given that individual policy measures all have shortcomings, the project investigates how mixes of measures could enhance climate policy. Thanks to a pluri-disciplinary approach, DECARB identifies desirable mixes that would allow Switzerland to reach climate neutrality by 2050.
First, a review of the academic literature shows that there are several market failures, barriers to decarbonisation and policy constraints that justify the use of instrument mixes rather than a stand-alone carbon tax. While the desirable mixes differ across sectors, given the different target actors and technologies, some carbon tax is found to play a key role in all of them.
Second, using a mathematical model of the Swiss economy, the researchers show that the deep decarbonisation induced by the mixes has a negligible impact on gross domestic product (GDP), in the order of 1‰. When complementary instruments are included in the policy landscape, the carbon tax rate required to achieve an ambitious emissions target can be divided by about two. On the other hand, a stand-alone carbon tax allows for the highest rebate to households among the scenarios considered.
Third, using an online survey, the team provides evidence that Swiss citizens have a strong preference for instrument mixes rather than a stand-alone carbon tax. Language region, number and type of cars owned, and perceived threat of climate change are found to be important predictors of instrument preferences.
Full report: Cocker, F., Thalmann, P., Vielle, M., Vöhringer, F., Weber, S. (2024). DECARB – Mixes of policy instruments for full decarbonisation by 2050. Project funded by the Energy-Economy-Society (EES) research programme of the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE), Bern.
Authors: Fleance Cocker (EPFL), Philippe Thalmann (EPFL)
Shutterstock: ID: 2463945033; Doidam 10




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenSWISS-JAPAN ENERGY DAYS 2024: COLLABORATION ON BREAKTHROUGH INNOVATIONS FOR FUTURE SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
The Swiss-Japan Energy Days 2024 conference, scheduled for September 10-11, 2024, at ETH Zürich and Swissnex in Japan, is set to address the pressing challenges in the energy sectors of both countries. Dr. Felix Moesner, Swiss Consul & CEO of Swissnex in Japan, discusses the importance of this event and its anticipated impact. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenThe Energy – Economy – Society (EES/EWG) research programme promotes application-oriented research in the field of energy policy. To this end the EES focuses on economic, social, psychological and political issues throughout the energy sector supply chain. EES elaborates calls to fund innovative socio-economic research projects that address relevant energy-policy questions for Switzerland. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenThe Energy – Economy – Society (EES/EWG) research program promotes application-oriented research in the field of energy policy. To this end, the EES focuses on economic, social, psychological and political issues throughout the energy sector supply chain. EES elaborates calls to fund innovative socio-economic research projects that address relevant energy-policy questions for Switzerland. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenA tour d’horizon of India’s energy transition and the role of energy storage
India provides unprecedented opportunities to scale solar and wind power, making it one of the forerunners of a world heading towards a sustainable future. However, there is one basic challenge that India must face: the intermittency of renewables. The article by Peter Freudenstein, an energy and climate change policy analyst and a Mercator Fellow, suggests methods that India can adopt to solve its problem. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenGeneral overview
China is both the world’s biggest clean energy investor and the world’s largest CO2 emitter. It is on track to becoming the world’s renewable energy superpower: China is the world’s largest producer, exporter and installer of solar panels, wind turbines, batteries and electric vehicles.
Even though renewable energy investments declined from $122 billion in 2017 to $86 billion in 2018, China still has by far the largest capacity. It also has a clear lead in terms of the underlying technology, with well over 150,000 renewable energy patents as of 2016, 29% of the global total. The next closest country is the U.S., which had a little over 100,000 patents, with Japan and the E.U. having close to 75,000 patents each.
The share of non-fossil fuels in China’s total electricity mix is on course to hit 32-34% in 2020. With increasing demand, China added about 40 GW of solar and 40 GW of coal in 2019. There is a lot of room for renewable energy, since coal’s share in China’s primary energy mix was still 58% in 2018 and electricity demand keeps growing. Weiterlesen




 4 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 4,75
4 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 4,75The ReFlex project aims at developing a replicability guideline for the deployment of technologically feasible, market based and user-friendly solutions for smart grids with a high level of flexibility. The focus was put on smart grid pilot projects with high level of renewable energy production, which are effectively and efficiently used locally through mixes of measures from voltage regulation, demand response, energy management and storage. Drawing on the learning experience among ReFlex partners, replicability-guidelines were elaborated to support the demo regions and the wider group of European smart grid stakeholders in deploying and advancing their smart grid initiatives. The project released the ReFlex Guidebook, a document that includes guidelines for the replicability of solutions for flexible smart grids. Weiterlesen




 1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00
1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00Energy efficiency is the first fuel in a modern, global energy system
Fatih Birol, Executive Director of the International Energy Agency IEA, presents the IEA market report on Energy Efficiency 2018 and emphasizes that energy efficiency needs to have a seat at the big table, when it comes to major global decisions about energy in the 21st century.




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenKontakt
Bundesamt für Energie
Pulverstrasse 13
3063 Ittigen
Postadresse:
Bundesamt für Energie
3003 Bern
Telefonnummern:
Hauszentrale +41 58 462 56 11
Pressestelle +41 58 460 81 52
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock Shutterstock
Shutterstock shutterstock
shutterstock ©Swissnex Japan
©Swissnex Japan Shutterstock
Shutterstock Shutterstock
Shutterstock Swissnex China
Swissnex China BFE
BFE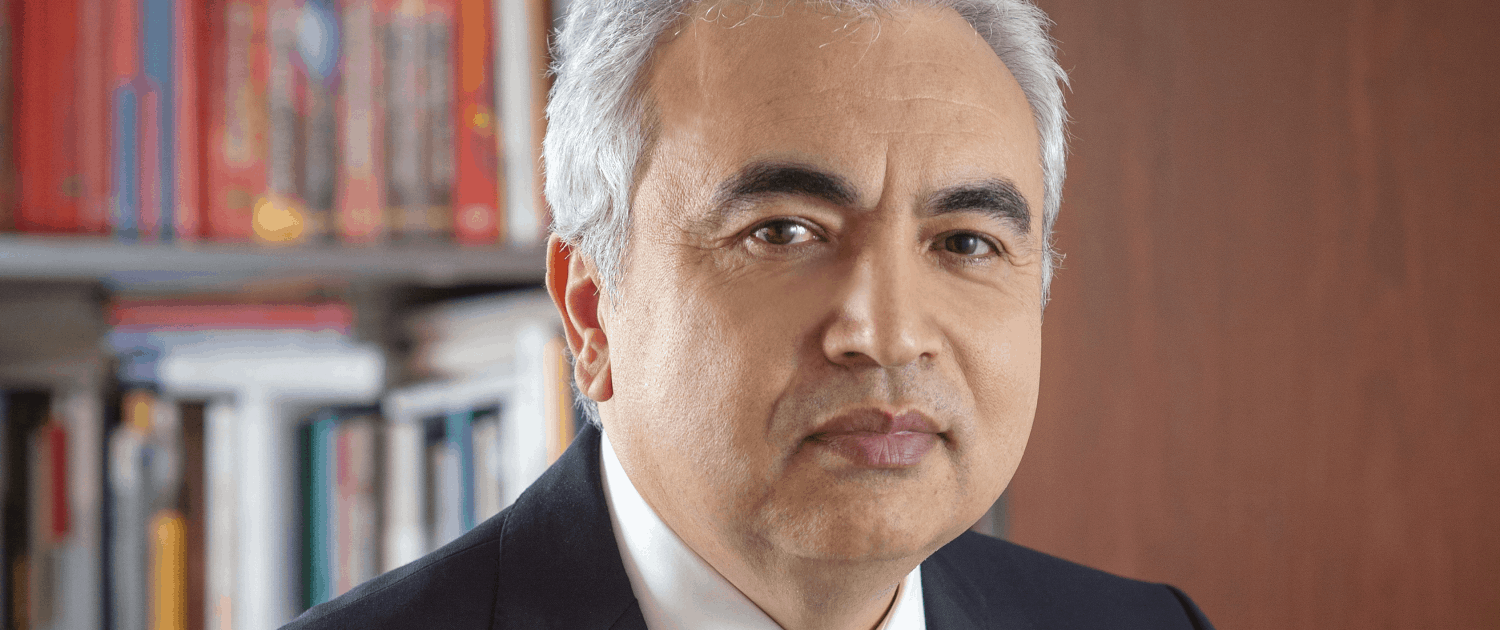 IEA
IEA