Die Ziele sind definiert, die Projekte gebündelt: Die ETH Zürich ist auf Expeditionskurs mit Ziel Netto-Null. Vieles ist noch ungewiss, doch eines ist klar: Es braucht Mut und Gestaltungswillen, um das Ziel zu erreichen. Gut, dass sich die ETH als Hochschule durch Innovation und Kooperation auszeichnet. Weiterlesen
Schlagwortarchiv für: resources
Reducing energy consumption, through new ways of living and working, efficient mobility behavior or a changed environmental awareness – this is the goal of the SWEET call “Living&Working”. To this end, the two selected consortia SWICE and LANTERN are developing, implementing and testing new approaches, methods and technologies in so-called „Living Labs“. Joëlle Mastelic, professor at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Western Switzerland and coordinator of LANTERN, and Marilyne Andersen, professor at EPFL and coordinator of SWICE, tell us where the focus of their research lies and what is distinctive about research in Living Labs. Weiterlesen




 1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00
1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00CROSSDat – An open energy data platform for Switzerland
How much energy do buildings consume per canton, per municipality? How big is the heating demand? How much electricity did Switzerland consume yesterday? How many Smart Meters are installed per municipality? In terms of data freely available on the energy sector – so called Open Energy Data -, Switzerland has a lot of catching up to do compared to other countries. Why is that? What are the obstacles? Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenThe extraction of gas molecules from a gas mixture and their adsorption onto a solid plays an important role in many industrial processes. In many cases, technical systems are used today for these adsorption processes that are oversized for their task. This consumes unnecessarily high amounts of adsorption materials, investment resources and energy. To avoid this, a team of researchers from the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts has developed a model and an associated guideline. They help process engineers to better design the appropriate dimensions of gas purification and gas recovery plants in proportion with requirements. The scientists estimate the potential energy savings at 25 to 30 percent.
Read the full specialist article (also in German): „Using Activated Carbon & Co Efficiently“.
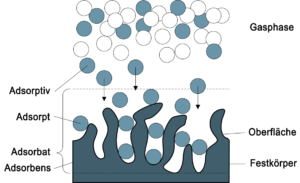
Benedikt Vogel, on behalf of the SFOE




 1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 1,00
1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 1,00General overview
China is both the world’s biggest clean energy investor and the world’s largest CO2 emitter. It is on track to becoming the world’s renewable energy superpower: China is the world’s largest producer, exporter and installer of solar panels, wind turbines, batteries and electric vehicles.
Even though renewable energy investments declined from $122 billion in 2017 to $86 billion in 2018, China still has by far the largest capacity. It also has a clear lead in terms of the underlying technology, with well over 150,000 renewable energy patents as of 2016, 29% of the global total. The next closest country is the U.S., which had a little over 100,000 patents, with Japan and the E.U. having close to 75,000 patents each.
The share of non-fossil fuels in China’s total electricity mix is on course to hit 32-34% in 2020. With increasing demand, China added about 40 GW of solar and 40 GW of coal in 2019. There is a lot of room for renewable energy, since coal’s share in China’s primary energy mix was still 58% in 2018 and electricity demand keeps growing. Weiterlesen




 4 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 4,75
4 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 4,75The Swiss initiative on Hydropower at IRENA Assembly – a success story
The Ministerial Plenary Session on Hydropower, held at the 10th General Assembly (GA) of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) on 12 January 2020, was a key success for the Swiss delegation. Switzerland, together with the International Hydropower Association (IHA), the World Bank, Norway and other IRENA member countries, co-organized the Ministerial Plenary Session. It built on the first ever IRENA Hydropower Event, which was initiated by Switzerland and took place at the 9th GA in January 2019. Weiterlesen




 3 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00
3 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00Worldwide Living Labs are increasingly adopted to address urban challenges. They are projects or experiments devised to design, test and learn from innovative socio-technical practices (i.e. “new ways of doing something”), with a diversity of stakeholders and in real-life conditions. However, they tend to focus on small-scale performance tests or technology-user interactions, and are mostly neglecting the larger social-institutional context that surrounds them. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenDie Energiestrategie 2050 hat sich zum Ziel gesetzt, die Jahresnutzung der Bioenergie auf 27‘800 Gigawattstunden bis im Jahr 2050 fast zu verdoppeln. Eine erfolgreiche Umsetzung dieses Ziels erfordert eine Priorisierung von Projekten in Regionen mit reichlichen Bioenergie-Ressourcen. Weiterlesen




 Noch keine Bewertungen
Noch keine BewertungenMechanics – the key to unlocking subsurface resources for energy supply and storage
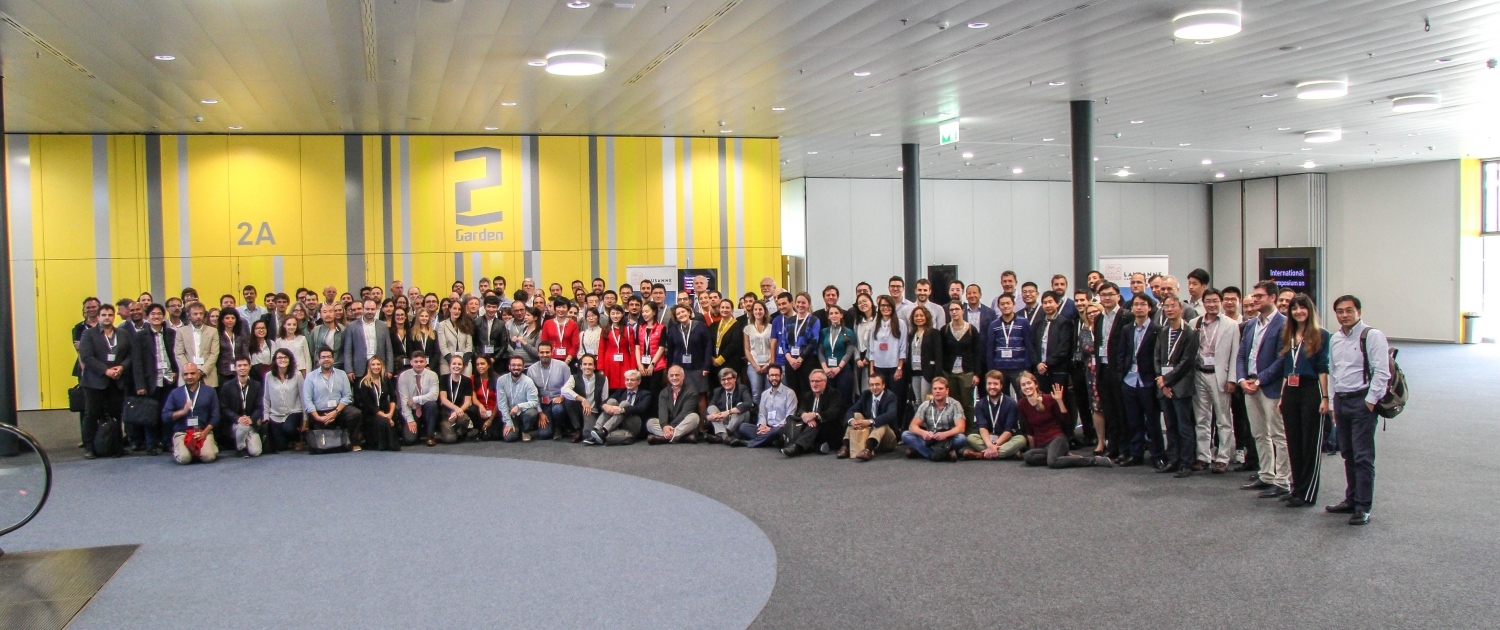
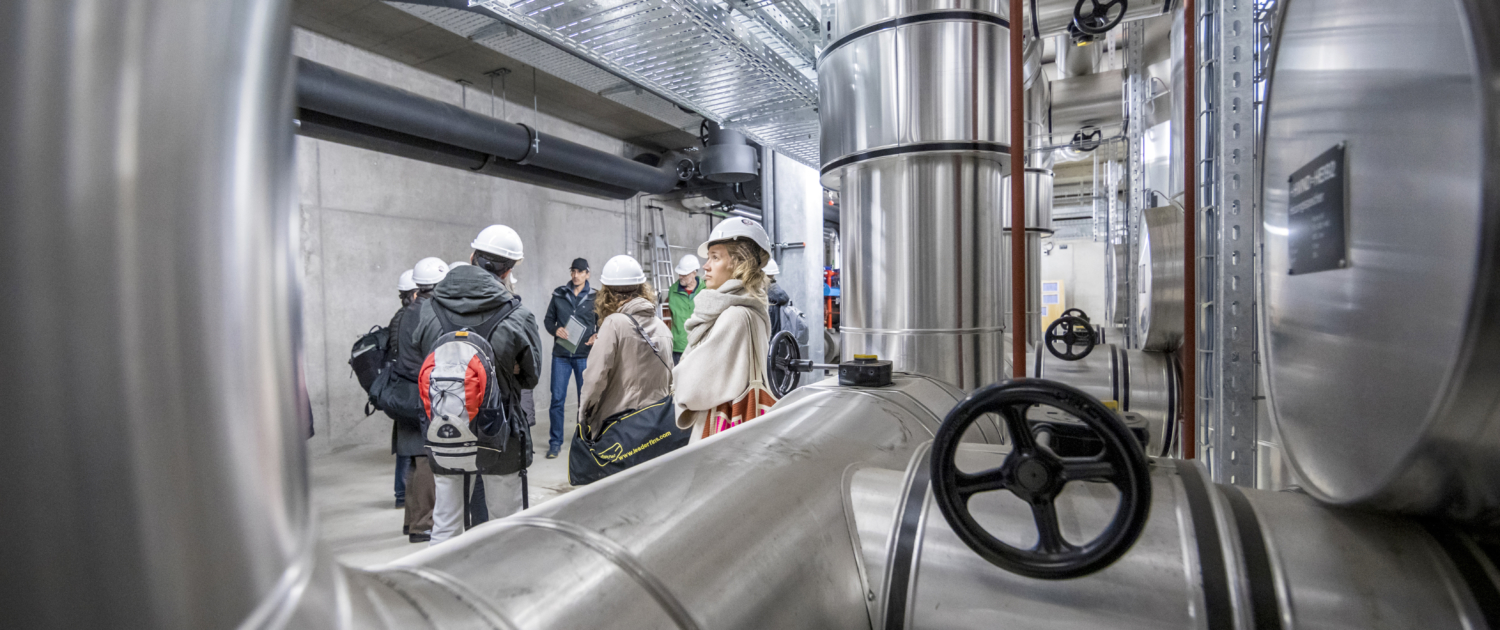
The International Symposium on Energy Geotechnics organized by EPFL’s Laboratory of Soil Mechanics brought together more than 250 research scientists and practitioners from 35 countries at the Swiss Tech Convention Centre in Lausanne to exchange ideas, practices and state-of-the-art developments. Weiterlesen




 4 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00
4 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 5,00MAtCH is a exchange program for cleantech start-ups between Switzerland and Massachusetts/USA, operated by the Massachusetts Clean Energy Center and the Swiss Federal Office of Energy. The Swiss born architect Eric Nelson (46) has joined the program in fall 2017. In this interview he summarizes his experiences. Weiterlesen




 1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 4,00
1 Vote(s), Durchschnitt: 4,00Kontakt
Bundesamt für Energie
Pulverstrasse 13
3063 Ittigen
Postadresse:
Bundesamt für Energie
3003 Bern
Telefonnummern:
Hauszentrale +41 58 462 56 11
Pressestelle +41 58 460 81 52
 ETHZ
ETHZ Shutterstock
Shutterstock shutterstock
shutterstock Shutterstock
Shutterstock Swissnex China
Swissnex China IRENA
IRENA SUPSI
SUPSI UNIGE
UNIGE
